学习了MongoDB,在这里记录一下,日后可以用来温习。
1.mongodb介绍及安装
2. 命令行使用
3.安全和权限控制
4.node中使用
5. node+mongodb结合的项目示例
一. mongodb介绍及安装
1. 介绍
官网:Building on the Best of Relational with the Innovations of NoSQL
MongoDB也有一个Ruby的项目MongoMapper,是模仿Merb的DataMapper编写的MongoDB接口,使用起来非常简单,几乎和DataMapper一模一样,功能非常强大。
MongoDB是一个介于关系数据库和非关系数据库之间的产品,是非关系数据库当中功能最丰富,最像关系数据库的。他支持的数据结构非常松散,
是类似json的bjson格式,因此可以存储比较复杂的数据类型。
Mongo最大的特点是他支持的查询语言非常强大,其语法有点类似于面向对象的查询语言,几乎可以实现类似关系数据库单表查询的绝大部分功能,而且还支持对数据建立索引。
所谓“面向集合”(Collenction-Orented),意思是数据被分组存储在数据集中,被称为一个集合(Collenction)。每个 集合在数据库中都有一个唯一的标识名,
并且可以包含无限数目的文档。集合的概念类似关系型数据库(RDBMS)里的表(table),不同的是它不需要定 义任何模式(schema)。
模式自由(schema-free),意味着对于存储在mongodb数据库中的文件,我们不需要知道它的任何结构定义。如果需要的话,你完全可以把不同结构的文件存储在同一个数据库里。
存储在集合中的文档,被存储为键-值对的形式。键用于唯一标识一个文档,为字符串类型,而值则可以是各中复杂的文件类型。
我们称这种存储形式为BSON(Binary Serialized dOcument Format)。
区别于关系型数据库,mongodb三个基本的概念:
- 数据库:数据库是一个物理容器集合。每个数据库都有自己的一套文件系统上的文件。一个单一的MongoDB服务器通常有多个数据库。
- 集合:集合是一组MongoDB的文档。它相当于一个RDBMS表。收集存在于一个单一的数据库。集合不执行模式。集合内的文档可以有不同的领域。通常情况下,一个集合中的所有文件是相同或相关的目的。
- 文档:文档是一组键 - 值对。文件动态模式。动态模式是指,在相同集合中的文档不需要具有相同的字段或结构组的公共字段的集合的文档,可以容纳不同类型的数据。
2. 安装
第一步:
推荐使用Homebrew安装brew install mongodb
注意: 因为MongoDB需要xcode编译,所以如果系统版本低的话,安装会有如下提示:
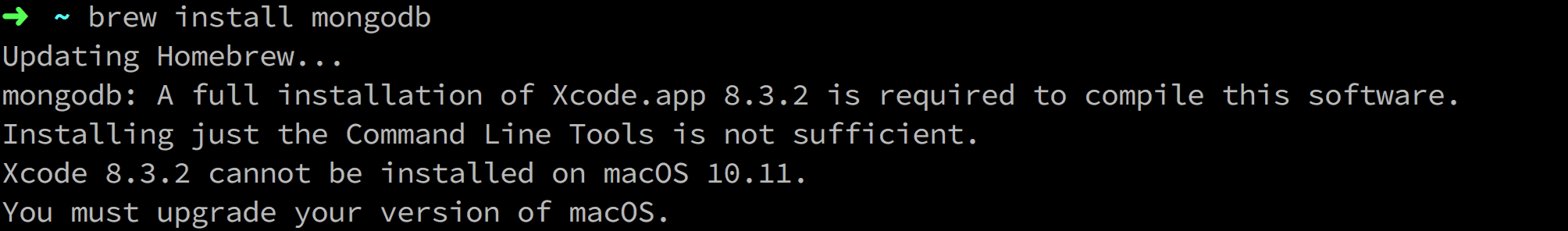
解决办法:brew search mongodb
brew install mongodb@3.4

第二步:
创建db库存放路径mkdir -p /data/db
sudo chown -R lishuna /data
配置config## /usr/local/etc/mongod.conf
systemLog:
destination: file
path = /data/dbLog/mongo.log
logAppend: true
storage:
dbPath = /data/db
net:
bindIp: 127.0.0.1
#mongodb3.4默认不开启命令行设置权限,需要单独配置。3.6是不需要下面的配置
security:
authorization: enabled
设置shell’s path路径 (e.g. ~/.bashrc or ~/.zshsrc)export PATH=<mongodb-install-directory>/bin:$PATH
推荐的可视化工具:robomongo
第三步:
启动服务mongod
二. 命令行使用
数据类型 https://docs.mongodb.com/v3.4/reference/bson-types/
CRUD操作
1.Insert API文档
insert
db.inventory.insert(
{ item: "canvas", qty: 100, tags: ["cotton"], size: { h: 28, w: 35.5, uom: "cm" } }
)insertOne
db.inventory.insertOne( |
- insertMany
db.inventory.insertMany([
{ item: "journal", qty: 25, tags: ["blank", "red"], size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" } },
{ item: "mat", qty: 85, tags: ["gray"], size: { h: 27.9, w: 35.5, uom: "cm" } },
{ item: "mousepad", qty: 25, tags: ["gel", "blue"], size: { h: 19, w: 22.85, uom: "cm" } }
])
2.Query API文档
find
db.inventory.find( {} )
1.运算符
{ <field1>: { <operator1>: <value1> }, ... }
db.inventory.find( { status: { $in: [ "A", "D" ] } } )
AND Conditions
db.inventory.find( { status: "A", qty: { $lt: 30 } } )
OR Conditions
db.inventory.find( { $or: [ { status: "A" }, { qty: { $lt: 30 } } ] } )
AND as well as OR Conditions
db.inventory.find( {
status: "A",
$or: [ { qty: { $lt: 30 } }, { item: /^p/ } ]
} )
查询的基础运算符
- $eq Matches values that are equal to a specified value.
- $gt Matches values that are greater than a specified value.
- $gte Matches values that are greater than or equal to a specified value.
- $in Matches any of the values specified in an array.
- $lt Matches values that are less than a specified value.
- $lte Matches values that are less than or equal to a specified value.
- $ne Matches all values that are not equal to a specified value.
- $nin Matches none of the values specified in an array.
更多: https://docs.mongodb.com/v3.4/reference/operator/query/
3. Update API文档
- db.collection.updateOne()
- db.collection.updateMany()
- db.collection.replaceOne()
- db.collection.update()
相关操作符:https://docs.mongodb.com/v3.4/reference/operator/update/
4. Delete API文档
- db.collection.deleteOne()
Delete at most a single document that match a specified filter even though multiple documents may match the specified filter.
- db.collection.deleteMany()
Delete all documents that match a specified filter.
- db.collection.remove()
Delete a single document or all documents that match a specified filter
help 可以帮助查询命令
三. 安全和权限控制(security)
MongoDB的访问控制能够有效保证数据库的安全,访问控制是指绑定Application监听的IP地址,设置监听端口,使用账户和密码登录
(一),访问控制的参数
1.绑定IP地址mongod --bind_ip ip_adress
指定MongoDB对外提供服务的绑定IP地址,只允许绑定的IP地址访问。
- 绑定端口号
mongod --port xxxx
指定连接MongoDB服务的端口,认监听的端口是27017
- 开启auth认证
mongod --auth
mongodb默认安装是不开启用户认证的,如果需要权限验证,则需要带上–auth参数。另外注意:MongoDB的3.4版本默认是开启命令输入参数开启验证的,需要在config里单独配置。配置如下:
authorization: enabled
4.权限认证
mongo -u <username> -p <password> --authenticationDatabase <dbname> |
说明:authenticationDatabase 为指定创建User的数据库;在特定的数据库中创建User,该DB就是User的authentication database。
例如:
//给Test库创建一个userAdmin用户
db.createUser(
... {
... user: "lsn_userAdmin",
... pwd: "lsn",
... roles: [ { role: "userAdmin", db: "Test" } ]
... }
... )
//登录: mongo -u lsn_userAdmin -p lsn -authenticationDatabase admin
use Test
//给Test库创建一个userAdmin用户
db.createUser(
... {
... user: "lsn_r",
... pwd: "lsn",
... roles: [ { role: "read", db: "Test" } ]
... }
... )
//登录: mongo -u lsn_r -p lsn -authenticationDatabase Test
(二),基于角色的访问控制(Role-Based Access Control)
首先需要切换到admin库,生成第一个用户:use admin
db.createUser(
... {
... user: "dba",
... pwd: "dba",
... roles: [ { role: "userAdminAnyDatabase", db: "admin" } ]
... }
... )
看下数据库预设的角色有哪些:详细API文档
- 数据库用户角色(Database User Roles):
- read:授予User只读数据的权限
- readWrite:授予User读写数据的权限
- 数据库管理角色(Database Administration Roles):
- dbAdmin:在当前dB中执行管理操作
- dbOwner:在当前DB中执行任意操作(dbAdmin和userAdmin的集合)
- userAdmin:在当前DB中管理User
- 备份和还原角色(Backup and Restoration Roles):
- backup
- restore
- 跨库角色(All-Database Roles):
- readAnyDatabase:授予在所有数据库上读取数据的权限
- readWriteAnyDatabase:授予在所有数据库上读写数据的权限
- userAdminAnyDatabase:授予在所有数据库上管理User的权限
- dbAdminAnyDatabase:授予管理所有数据库的权限
- 集群管理角色(Cluster Administration Roles):
- clusterAdmin:授予管理集群的最高权限
- clusterManager:授予管理和监控集群的权限,A user with this role can access the config and local databases, which are used in sharding and replication, respectively.
- clusterMonitor:授予监控集群的权限,对监控工具具有readonly的权限
hostManager:管理Server
- 超级管理员 (Superuser Roles)
- root:readWriteAnyDatabase, dbAdminAnyDatabase, userAdminAnyDatabase, clusterAdmin, restore, and backup。
示例:db.createUser(
... {
... user: "lsn_userAdmin",
... pwd: "lsn",
... roles: [
... { role: "userAdmin", db: "Test" }
... ]
... }
... )
四、node中使用
node中在连接mongodb数据库的时候,一般使用第三方提供的中间件,如:mongodb、mongolass、mongoose等。
对比:https://blog.csdn.net/hsany330/article/details/78805570
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/24308524
1.连接数据库
var mongoose = require('mongoose'); |
2.创建集合
var sm = new mongoose.Schema({ |
3.插入数据
users.insertMany([{ |
4.更新数据
users.update({loginId: '18501364356'},{ |
5.查询数据
users.find({ |
6.删除操作
users.deleteMany({ |
5. node+mongodb结合的项目示例
https://github.com/bailicangdu/node-elm

